Asphalt roads are prone to cracking and deterioration over time due to traffic stress, temperature changes, and water infiltration. Traditional road repairs often involve laying a new layer of asphalt over the old road surface. However, without additional reinforcement, cracks from the old pavement can quickly resurface, and water can seep down to weaken the road base. To address these issues, modern road construction and repair increasingly use fiberglass mat with mesh as a reinforcement layer. This material, placed between layers of asphalt, helps create longer-lasting, more resilient roads by adding strength and preventing water and cracks from damaging the pavement below. In this article, we explain what a fiberglass mat with mesh is, how it works in asphalt paving, how it’s applied, and the benefits it offers in extending the lifespan of asphalt roads.

What is This Material?
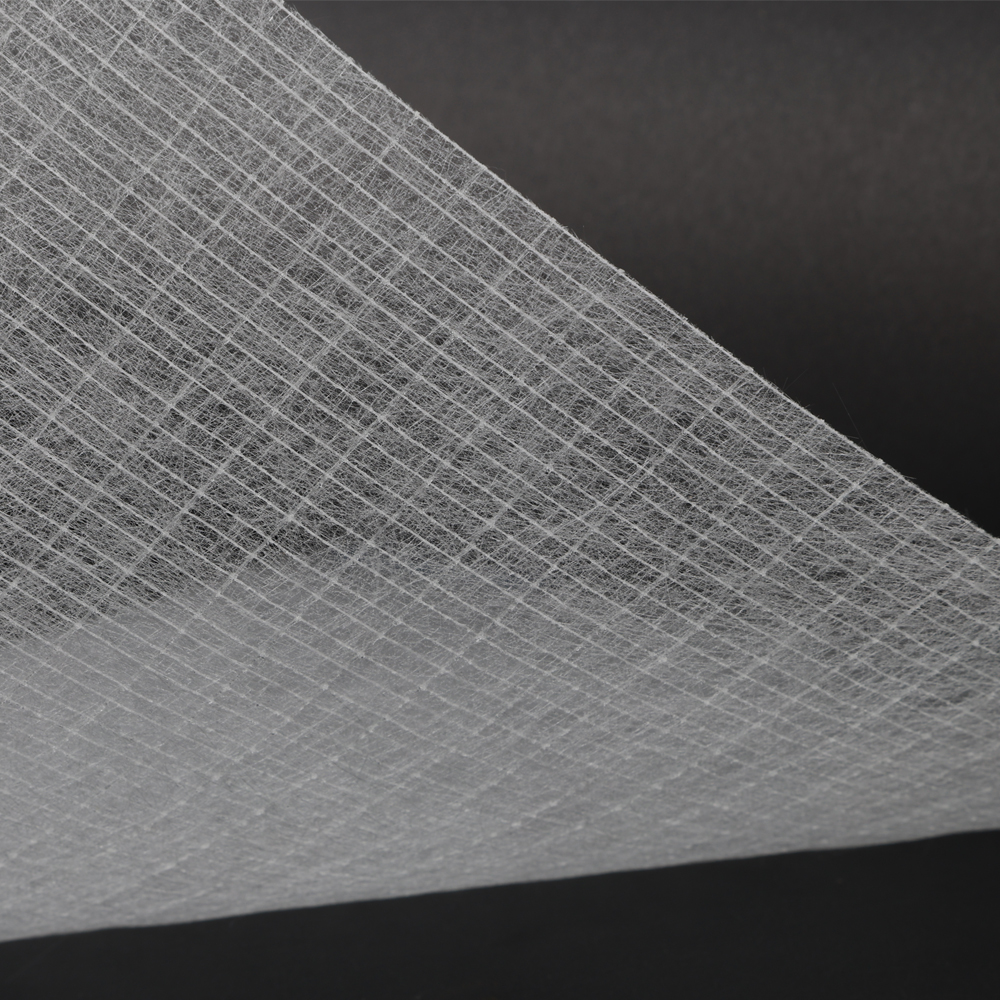
A fiberglass mat with mesh is a type of geosynthetic paving material designed to reinforce asphalt pavements. In simple terms, it is a sheet or layer made up of fiberglass strands woven into a mesh and often combined with a non-woven fabric backing. This combination creates a strong, flexible mat that can be laid between asphalt layers. The fiberglass mesh provides high tensile strength, while the fabric absorbs asphalt binder and forms a bond with the pavement.
Due to its very characteristic, it is also sometimes called asphalt paving mats, paving fabrics or geogrids, depending on their design. In all cases, the purpose remains the same. which is to reinforce the asphalt and create an additional protective layer within the road. Unlike simple asphalt overlays, which can only add limited life to a road, a fiberglass mesh interlayer significantly improves the pavement’s performance. It does this by adding a hidden strength to the road that isn’t present in asphalt alone. In fact, such interlayers have been shown to extend the life of new asphalt overlays by many years – in some studies, by as much as a decade longer.
How Exactly Does It Work?
Fiberglass mesh mats work by combining the strengths of different materials to improve pavement performance. Asphalt by itself is excellent in compression but relatively weak in tension. Fiberglass, on the other hand, is very strong in tension but cannot by itself support vehicle loads. When the two are combined, the road benefits from both: the asphalt provides a solid, load-spreading surface, and the fiberglass mesh provides tensile reinforcement, much like steel rebar does in concrete . This composite action means the pavement can resist cracking much better than asphalt alone.
Most importantly, the fiberglass interlayer targets a common failure mode in asphalt roads: reflective cracking. Reflective cracks occur when an existing crack or joint in the old pavement beneath propagates up through the new overlay, causing the fresh surface to crack along the same lines. A fiberglass mesh mat intercepts these cracks. When a crack from below reaches the stiff fiberglass mesh, the energy of the crack is spread out horizontally within the mat instead of continuing straight up to the surface . In other words, the crack is “turned” and dissipated within the reinforcement layer. By the time it might reach the top layer, much of its force is gone, and it may not appear at all for a long time.
Another way fiberglass mats work is by creating a moisture barrier. Because the fiberglass mat gets saturated with asphalt, it forms a water-resistant layer within the pavement. This waterproofing effect is crucial: it prevents water from seeping down through cracks and pores into the lower layers of the road. Water intrusion is a major cause of road damage – it can weaken the base layers and cause potholes or freeze-thaw damage in cold climates. By keeping water out, the interlayer protects the pavement structure from one of its worst enemies.

Fiberglass mat with mesh has become an invaluable tool in asphalt road building and repair, providing an informative example of how modern materials can enhance traditional construction. By inserting a thin yet strong fiberglass-reinforced layer into the pavement, engineers have found a way to greatly improve road durability without massive cost or effort. This fiberglass interlayer strengthens the asphalt, prevents cracks from rapidly propagating to the surface, and seals out damaging moisture, thereby tackling the main causes of pavement failure . The result is that asphalt roads reinforced with fiberglass mesh mats stay in better condition for longer, extending the time between major rehabilitations.
